| Block Group: | Logic |
| Icon: |
|
Returns one value if all its input properties are TRUE and another value if one or more input properties is FALSE.
An And block is simply an If block where the op property is set to "and".
One common use for the "and" function is to expand the capability of a block that performs a logical test. For example, the If block performs a logical test to evaluate whether a condition is true or false. By using the "and" function as the op property of the If block, you can test many different conditions instead of just one.
You can add more input n properties by clicking the plus sign, and delete them by clicking the minus sign. There is no limit to the number of input properties you can have. When you add a new input property, it is true by default. The input properties must evaluate to logical values, such as TRUE or FALSE. If the input properties contain no logical values, the And block returns the else value.
These properties can take input and give output.
op specifies the comparison, arithmetic, or text operator to apply to the input values. The operator is used with inputs to form an expression that can be evaluated to TRUE or FALSE. By default, the op value of an And block is "and". The block will not act as described on this page if you change this property.
input n specifies one of the input values. All input n values must evaluate to TRUE for the And block to return the then value. For example, "input 0 AND input 1" is a comparison expression. If the values input 0 and input 1 are TRUE, the expression evaluates to TRUE and the And block outputs the then value. Otherwise, if one of the inputs is FALSE, the And block outputs the else value. If input n is a number, a value of 0 evaluates to FALSE and a value of 1 evaluates to TRUE. Add more input n properties by clicking the plus sign.
then specifies the value to return if all of the input properties evaluate to TRUE.
else specifies the value to return if one or more of the input properties evaluate to FALSE.
These properties can give output. They cannot take input.
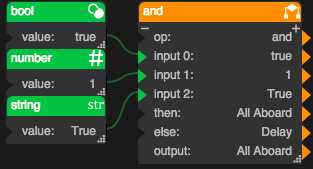
If the values in input 0, input 1, and input 2 are true, the output is "All Aboard". Otherwise, the output is "Delay".
|